Obesity Research Solutions
Learn about innovative tools to study the mechanisms of obesity and accelerate the development of safe, effective therapies. We offer solutions for measuring GPCR signaling, energy metabolism, and inflammation.
We're here to help solve challenges in your research—just ask us!
Obesity and Drug Discovery
Obesity is a multifaceted metabolic disease influenced by genetic, hormonal, and inflammatory factors. Drug discovery efforts focus on targeting key pathways that regulate appetite, energy metabolism, and fat storage, with increasing attention on GPCRs, hormone signaling, inflammatory cytokines, and muscle metabolism.
Recent advancements in metabolic and inflammatory biomarkers, functional receptor assays, and myostatin inhibition are shaping the next generation of obesity therapeutics. Understanding these complex mechanisms is critical for developing effective treatments that address not just weight loss, but also metabolic health and obesity-related comorbidities.

GPCRs
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) play a critical role in obesity by mediating key physiological processes such as appetite regulation, energy expenditure, and metabolic homeostasis. As targets for hormones like GLP-1, GPCRs are central to many obesity therapies.
Explore our comprehensive tools for GPCR research, including assays for ligand binding, protein-protein interactions, cAMP signaling, receptor internalization and gene expression.
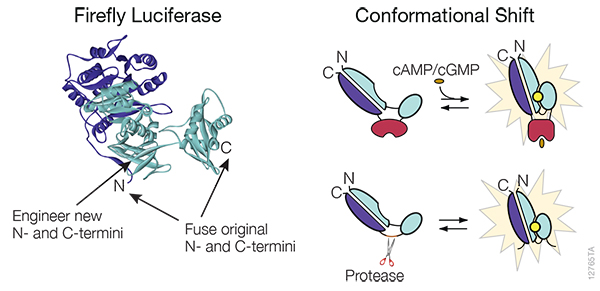
Monitor Agonist-Induced GPCR Internalization with HiBiT
Tag your GPCR of interest with a small, luminescent HiBiT peptide via CRISPR gene editing. Upon agonist binding, receptor internalization can be quantified in real-time through a luminescence assay, offering a sensitive and scalable method to study receptor trafficking and signaling dynamics.

Schematic of assays utilizing the HiBiT/LgBiT reporter for monitoring ligand-induced GPCR internalization. See details in this publication: The luminescent HiBiT peptide enables selective quantitation of G protein–coupled receptor ligand engagement and internalization in living cells.

Measurement of agonist-induced internalization of HiBiT-tagged GLP-1R. See details in this poster: Advancing Therapeutic Strategies for Obesity: Innovative Bioluminescence Assays for Monitoring GPCR Dynamics
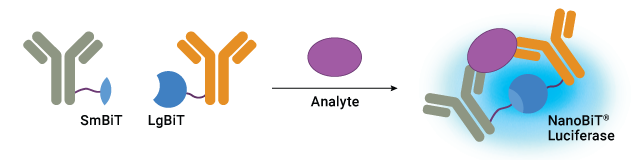
Analyze β-Arrestin Recruitment in Real Time
Our NanoBiT® Technology enables real-time monitoring of β-arrestin recruitment to GPCRs by fusing the receptor and β-arrestin with complementary luciferase fragments. Upon receptor activation and β-arrestin binding, the fragments reconstitute a functional luciferase enzyme, producing a luminescent signal that directly correlates with β-arrestin recruitment.


Real-time monitoring of agonist-induced β-arrestin recruitment to GLP-1R. See details in this poster: Advancing Therapeutic Strategies for Obesity: Innovative Bioluminescence Assays for Monitoring GPCR Dynamics
Measure Changes in cAMP Levels in Real Time
Our cAMP assays provide a sensitive and high-throughput solution for monitoring agonist-induced changes in intracellular cAMP levels, enabling precise characterization of GPCR signaling dynamics.

Monitoring GLP-1R agonist-induced changes in cAMP levels in real time using GloSensor™ technology. See details in this poster: Advancing Therapeutic Strategies for Obesity: Innovative Bioluminescence Assays for Monitoring GPCR Dynamics
Energy Metabolism and Regulation
Energy metabolism is central to obesity research, encompassing processes that regulate glucose and lipid homeostasis. Understanding these interconnected pathways is critical for identifying therapeutic targets that restore metabolic balance. Assays for measuring key biomarkers like insulin secretion, glucose uptake, and lipid metabolism help understand the complexities of energy regulation and develop more effective obesity treatments.
Explore our extensive portfolio of sensitive bioluminescent assays for measuring metabolism.
Measure Insulin and Glucagon
Measuring hormone levels is essential for understanding the dysregulation of glucose and lipid homeostasis in obesity, as insulin resistance is a hallmark of the disease. Our Lumit® Immunoassays for measuring insulin or glucagon are simple, no-wash luminescent assays that enable rapid and accurate analysis of secretion and signaling in obesity research.

Measure Glucose
Glucose metabolism plays a central role in obesity research, as dysregulated glucose levels and impaired uptake are key drivers of insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction. Understanding glucose detection and uptake mechanisms provides critical insights into obesity-related conditions and potential therapeutic interventions. Our Glucose-Glo™ and Glucose Uptake-Glo™ Assays are a fast, selective and sensitive method for measuring glucose.

Measurement of glucose uptake in adipocyte cells treated under various conditions using Glucose Uptake-Glo™ Assay. Cytochalasin B is a glucose transporter inhibitor which decreases glucose uptake. LY294002, a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor, is an essential insulin signaling enzyme which decreases glucose uptake relative to insulin alone.

Measurement of gluconeogenesis and inhibition by insulin using Glucose-Glo™ Assay. Microtissues (InSphero) formed from 2000 iCell® Hepatocytes 2.0 (CDI) were washed and incubated with 10mM lactate, 2μM forskolin, and a titration of insulin for 6 hours.
Measure Lipid Metabolism
Obesity is characterized by an imbalance between lipogenesis, the process of synthesizing and storing fat, and lipolysis, the breakdown of stored lipids for energy. Dysregulation of these pathways contributes to excess fat accumulation and metabolic dysfunction. Measuring key markers of lipogenesis and lipolysis provides valuable insights into adipose tissue dynamics and helps identify potential therapeutic strategies to restore metabolic balance.
Our lipid metabolism assays provide sensitive, simple methods to measure lipolysis and lipogenesis by detecting glycerol, triglyceride, cholesterol and cholesterol esters.


Measurement of lipolysis in response to insulin using Glycerol-Glo™ Assay. 3T3-L1 MBX adipocytes were washed and treated for 90 minutes with different combinations of isoproterenol (25nM) and insulin (150nM).

Measurement of triglyceride in 3D liver microtissues using Triglyceride-Glo™ Assay. 3D InSight Human Liver Microtissues (InSphero) were incubated with either physiological (LG/LI) or supraphysiological (LG/HI) levels of glucose and insulin and supplementation with either free fatty acids bound to BSA (FFA) or low density lipoprotein plasma fraction (LDL).
Researcher Spotlight
Read this blog to learn how Jon Campbell’s lab at Duke University is using our technology to characterize incretin biology. See details in the publications below, including using NanoBRET™ technology to measure ligand-induced Gs recruitment, Lumit® technology to quantitate insulin and glucagon, and GloSensor™ technology to monitor cAMP levels.
The incretin co-agonist tirzepatide requires GIPR for hormone secretion from human islets
GLP1-mediated delivery of tesaglitazar improves glucose metabolism in mice
Incretin-Related Hormones
Hormones such as GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon are key regulators of metabolism, appetite, and energy balance, making them critical targets in obesity drug discovery. Measuring their activity provides valuable insights into metabolic function and therapeutic potential.
Measure Receptor Activity with Bioassays
Our bioassays use engineered cells to link hormone receptor activation to a luminescent reporter, providing a sensitive and quantitative readout of receptor activity. When incretin-related hormones like GLP-1, GIP, or glucagon bind to their receptors, intracellular signaling pathways trigger luciferase expression, producing a measurable signal. These assays enable researchers to assess receptor function, optimize drug candidates, and explore metabolic pathways critical for obesity treatment.
Contact our Tailored R&D Solutions Team about assays for GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptors. We can even help you create a bioassay for your hormone of interest!




Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a key driver of metabolic dysfunction in obesity, with adipose tissue secreting cytokines like TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β that disrupt insulin signaling and fuel disease progression. Measuring these biomarkers is essential for understanding obesity-related inflammation and developing targeted therapies.
Quantify Key Inflammation Markers
Lumit® Cytokine Immunoassays provide a simple, no-wash solution for quantifying key inflammatory markers like TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in obesity research. These luminescent assays enable researchers to accurately measure cytokine secretion in adipose and immune cells, offering valuable insights into the role of inflammation in metabolic dysfunction.

Detection of IL-2, IL-6, IFN-γ and TNF-α with the corresponding Lumit® Cytokine Immunoassay. Human PBMCs were plated in a 96-well plate in 100µl and treated for 24 hours with cell stimulation cocktail (CSC), lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or R848.
Myostatin
Myostatin, a negative regulator of muscle growth, has emerged as a potential target in obesity and metabolic disease research. Inhibition of myostatin signaling may promote muscle mass, enhance energy expenditure, and improve metabolic health, making it an attractive avenue for obesity therapeutics.
Measure Myostatin Inhibition
Our Myostatin Bioassay allows easy detection of myostatin inhibition. Contact our Tailored R&D Solutions Team for more information.

Myostatin Bioassay cells were treated with titrations of anti-myostatin blocking antibody landogrozumab in the presence of EC80 of myostatin. After 5 hours, Bio-Glo-NL™ reagent was added and plates were read on a GloMax® Discover Microplate Reader.
Services for Obesity Research
Need customized tools or expert guidance to support your obesity research? Our Tailored R&D Solutions Team is here to help! Our services include:
Custom Assay Development
- Development of bioassays for receptors or hormones of interest
- GPCR functional assays (e.g., ligand binding, internalization, β-arrestin recruitment)
- Custom cytokine detection assays for studying inflammation in obesity
Screening & Profiling Services
- High-throughput screening for GPCR modulators (e.g., agonists, antagonists, biased ligands)
- Functional screening of metabolic pathway targets (e.g., insulin signaling, lipid metabolism, energy balance)
- Cytokine profiling to assess obesity-driven inflammation